Bond Yield vs. Gold in fact competes with Treasury bonds.
/DurationandConvexitytoMeasureBondRisk2-0429456c85984ad3b220cd23a760cda5.png) Duration And Convexity To Measure Bond Risk
Duration And Convexity To Measure Bond Risk
Bond prices and yields act like a seesaw.
Bond price vs yield. If the yield on all 10 year government bonds trading in the secondary market is 2 per cent the same as the interest payments in our bond then the price of our bond will be 100 and the yield on our bond will also be 2 per cent. But when it happens its normally the result of a significant countervailing force. Yield is the income that a fund pays on either a monthly or quarterly basis.
Bond prices and yields can be calculated in several different ways depending on the type of bond and the definition of yield youre using. The negative relationship between gold and interest rates imply positive correlations with bond prices since the price of bonds is negatively related to. In this case the force in question is the current trajectory of US.
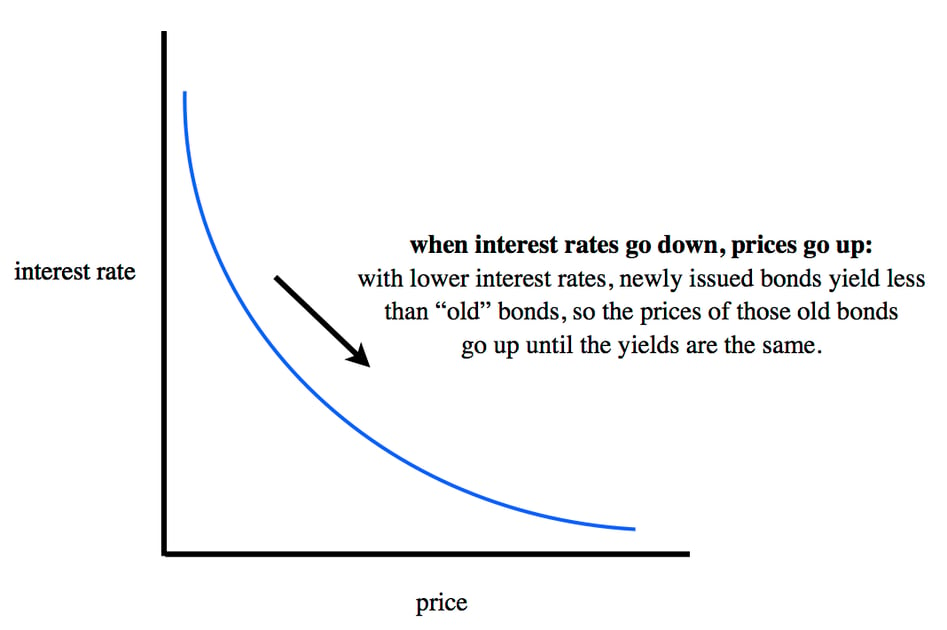
In this instance the bonds price would drop from 950 which gives a 526 yield to approximately 90909 which gives a 10 yield. This means that now bonds have a market price of 1500 the effective interest rate is 50 1500 333 Therefore because demand for bond rises the price of bonds rises and the effective interest rate yield falls. When bond yields go up prices go down and when bond yields go down prices go up.
If the rate of interest being paid on newly issued bonds stands at 8 a bond buyer would get paid 80 annually for each 1000 investment in one of those bonds. Bond prices and yields move in opposite directions which you may find confusing if youre new to bond investing. The investor can either take this income in the form of a check or reinvest it back into the fund to buy new shares.
Stock Prices Rising Rates. Bond Yields vs. The relationship between bond prices and bond yields is rather transparent.
The general rule of thumb for bonds is that bond prices move in the opposite direction of interest rates. For example assume an investor purchases a bond that matures in five years with a 10 annual coupon rate and a face value of. Yield to maturity includes both the interest payments you receive from a bond along with the capital gain you receive at maturity if any.
It is based on the interest rate and. Alternatively the causality of the relationship between yield to. Price Yield to Maturity Yield to maturity is the percentage of total return you can expect to receive when you buy a particular bond at a specific price.
It is considered as a long-term bond yield but is expressed as an annual rate. The yield on a bond that is sold for a price other than its face value is determined by dividing the annual interest payment by the price of the bond. When bond prices fall the.
A corporate bond with a 1000 face value that pays seven percent interest would have a yield of 70 or seven percent. Bonds are priced to yield a certain return to investors. In other words a bonds price is the sum of the present value of.
Benchmarks exist to track bond yields and serve as a. A bonds yield is the return that the investment generates over a year. The relation between bond price and Yield to maturity YTM YTM is the total return anticipated on a bond if the bond is held until its lifetime.
If Government cut Interest rates Suppose when the bond is issued the Bank of England base rate is 5. In other words a bonds price is the sum of the present value of each cash flow wherein the present value of each cash flow is calculated using the same discount factor. If that bond buyer instead bought your old 6 bond for the price you originally paid that bond would yield 20 less per year when compared to bonds on the market.
Indeed the rising 10-year yield. A bonds yield is the discount rate that can be used to make the present value of all of the bonds cash flows equal to its price. And since gold doesnt offer a yield yield-seeking investors tend to favor bonds over gold whenever bond rates are rising.
There are various ways to calculate yield which can be a source of confusion for many investors. Now that we have an idea of how a bonds price moves in. A bond that sells at a premium where price is above par value will have a yield to maturity that is lower than the coupon rate.
Both stock prices. As bond prices increase bond yields fall. Basically YTM is the internal rate of return of an investment in the bond if the following two conditions are satisfied.
Imagine that investors require a yield of 2 per cent to invest in a government bond.
